Mosquitoes are significant vectors of numerous diseases and endanger the health and economies of entire regions. Qista can help control mosquitoes across a large area in a way which is both effective and entirely environmentally-friendly.
Across the world, numerous infectious diseases are transmitted to humans or animals through mosquito bites alone. They represent a real danger for the health of entire populations and the development of the countries affected.
The solutions are costly and often polluting. Global warming is just increasing the health risk.


Thanks to its experience and years of research, Qista can now offer a mosquito solution which protects people from epidemics without posing a danger to human beings or ecosystems.
Qista developed its totally environmentally-friendly solution to control mosquitoes effectively across a large area, whatever the region or the scale in question.
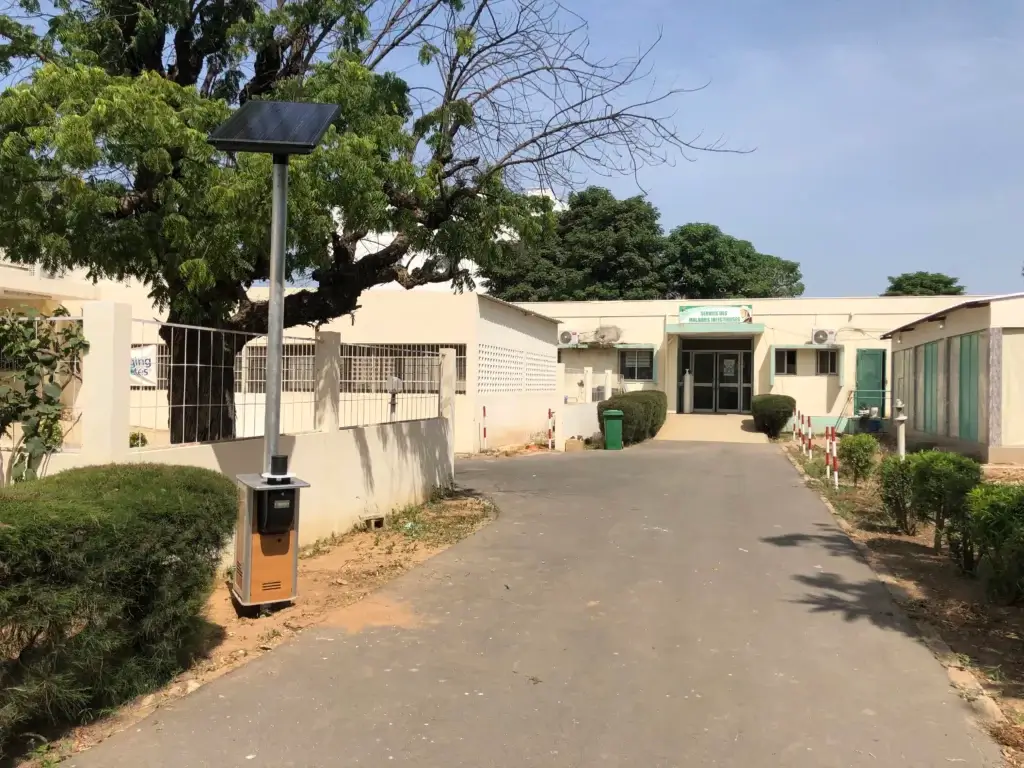
This has been the case in Kaolack, Senegal. The town has benefited from the installation of 104 green mosquito traps to prevent malaria, alongside the National Malaria Prevention Programme.

A professional, patented, environmentally-friendly and sustainable mosquito solution for controlling mosquitoes.
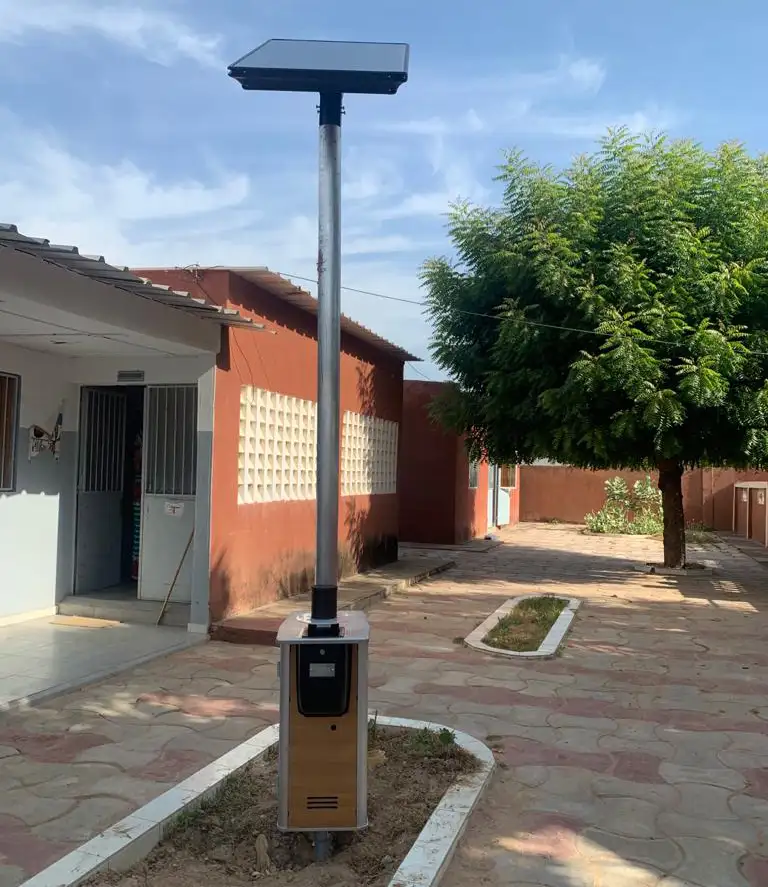
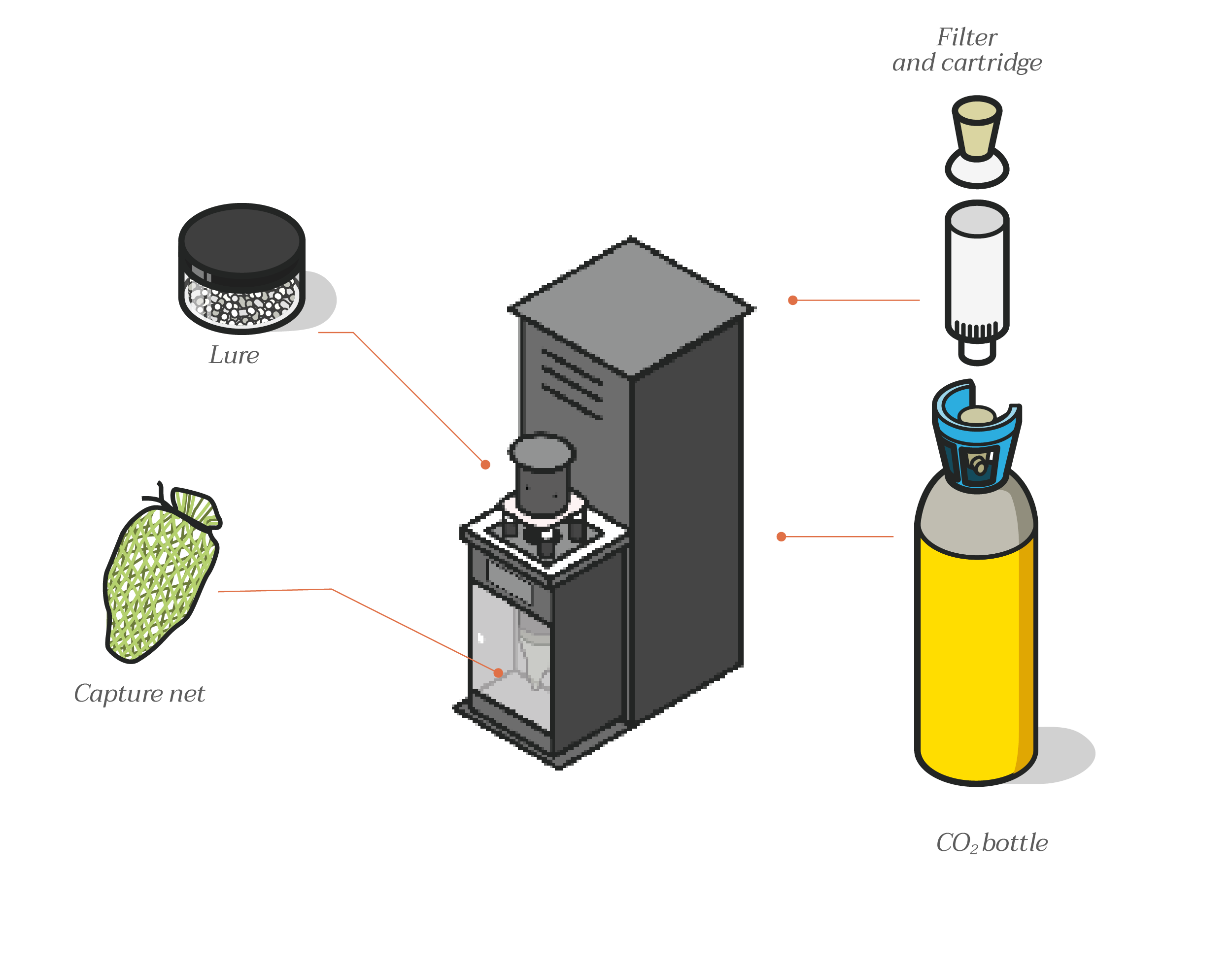
Qista’s mosquito traps simulate human presence to attract and trap the mosquitoes. Each trap has a range of up to 60 metres (i.e. a surface area of approximately 1 hectare). Very large areas can therefore be protected in a chain.
Large-scale protection
Qista’s solution means that it is possible for health organisations to control mosquitos across large areas without having an impact on ecosystems and without posing a danger to people.
To create real protection barriers and push mosquitoes away from a town or a farm, the traps can be installed at regular intervals along the boundary between the area to be protected and the area where mosquitoes reproduce.
Such large-scale control of mosquitoes means that the bite rate is significantly reduced: -88% according to research carried out in 2015 by the Ecosystems Department of the Centre de recherche de la Tour du Valat. This considerable drop in the number of mosquito bites leads de facto to a reduction in the spread of diseases.
Qista’s solution responds to both health problems and the WHO’s recommendations on vector control:
Qista’s solution is also part of an agro-economic and committed ecological approach to the issue:
Qista’s green mosquito control is therefore an economic investment creating growth. With Qista, the number of bites per hour dropped from 91.2 to 10.2*, i.e. an 88% reduction of the problem (source: Dr. Brigitte Poulin, Institut de recherche de la Tour du Valat).
Qista is working with a number of bodies, such as the Centre de Recherche de la Tour du Valat in the Camargue region of France, to continue its research into mosquitoes and improve its solution.
As real tools for health protection, a range of new features can be provided to organisations and the appropriate authorities:
A number of test communities have already benefited from the progress Qista is making in terms of vector control. Arranging a set of traps strategically throughout a town or neighbourhood does more than just chase mosquitoes away: you can comprehensively monitor infestation levels thanks to cross tabulation of the cumulative data provided by the Qista software.
Collected within the same software, this data is processed, cross tabulated and interpreted so as to constitute “big health data”. This data is essential for tackling the health and economic challenges facing certain regions. The aim is to direct and prioritise vector control and climate change action.
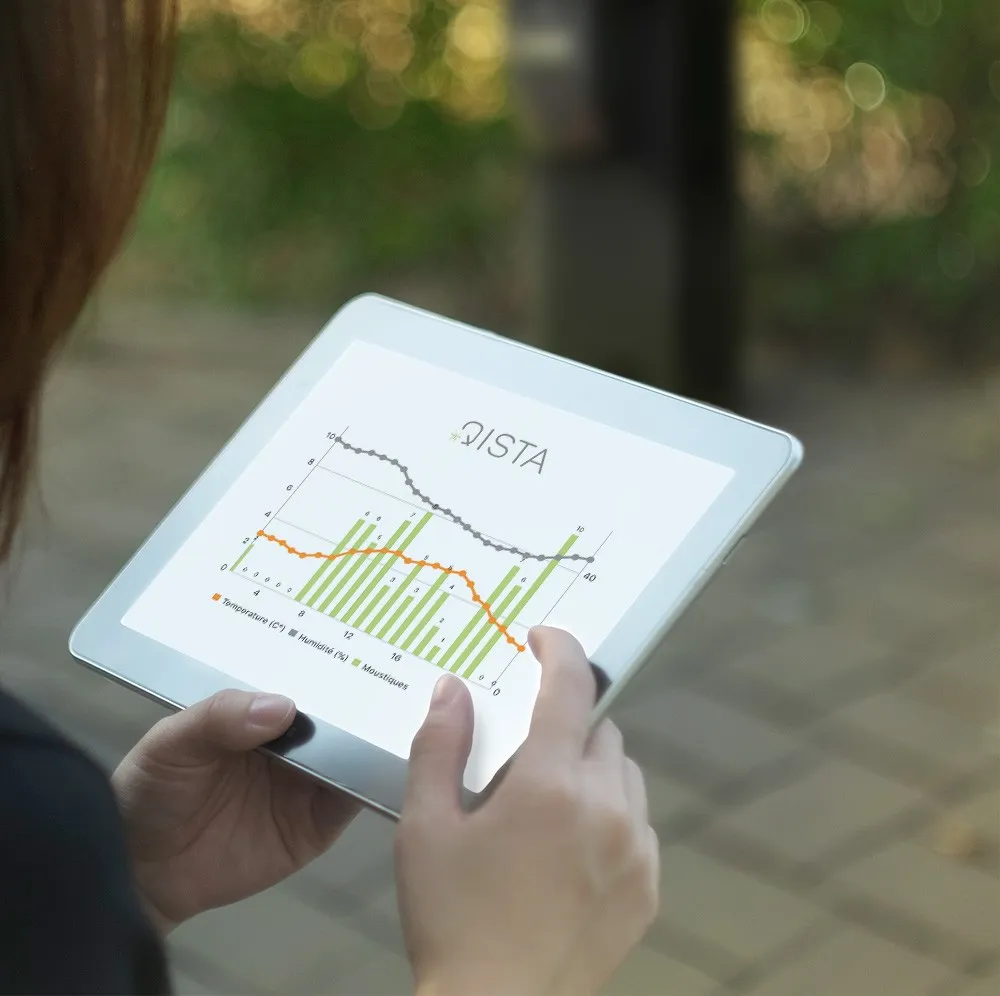

Thanks to predictive analytics and early diagnosis of epidemics, Qista is now playing an important role in preventing vector-borne diseases.
Its technology, which is unique across the world,means that it is possible to analyse the proliferation of mosquitoes and cross-tabulate that data with health information so as to predict the risks of epidemics and enable the health authorities in the areas concerned to take the necessary action.
Qista and vector control: the facts
The vector control department of the INHP in Côte d’Ivoire recognises that Qista’s mosquito traps are an effective tool for vector control and recommends their use.
Within the framework of the MONIPREV project, more than 100 Qista traps have been installed to reduce the rate of mosquito bites and also ensure monitoring and analysis of data gathered on the ground.

The predictive analytics provided by Qista is in-depth analysis of proliferation and capture data to model mosquito flows. These modelled flows mean that predictions can be made about the evolution of mosquito populations in the years to come, be that in terms of the number of individuals, the geographical areas infested or any potentially transmissible diseases.
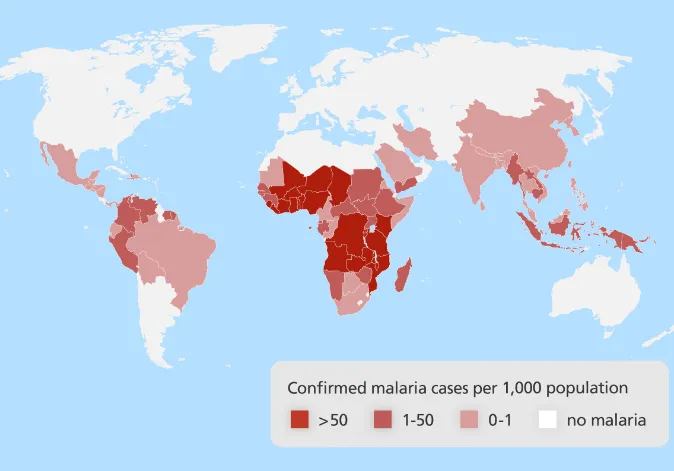
Mosquitoes are present on 5 continents, affect the living environments of more than half the world’s population and are responsible for pandemics.
In many countries, mosquitoes are synonymous with the spread of deadly diseases and considerable financial expenditure to treat those who fall ill. Mosquitoes on their own cause several hundred thousand deaths every year. According to the WHO, there are allegedly 390 million cases of Dengue every year.
Malaria caused 435,000 deaths in 2017.*
* According to the WHO Source of the map: World Malaria report 2014
The WHO therefore recommends introducing vector control strategies to prevent or reduce the spread of these diseases.
Preventive action means that it is possible to limit the number of breeding areas and therefore the reproduction of mosquitoes near areas where people live. But they have limitations when mosquitoes are able to reproduce in natural areas.
The elimination of mosquitoes in their larvae or adult state (curative control) using insecticides clearly reduces the number of individuals which risk spreading diseases. However, these treatments are not without consequences: some products are toxic for people or animals. Others pollute and damage ecosystems. Even the targeting of these products can be called into question because they destroy the larvae of other, inoffensive species. Moreover, it appears that mosquitoes are now demonstrating resistance to some types of insecticide, making them progressively less effective.
As well as posing a risk to the health of people and animals, and causing damage to ecosystems, these chemical methods for controlling mosquitoes can prove to be very costly and are not always sustainable.

Across the world, mosquitoes are the cause of viral and parasitic diseases. And although these diseases involve person-to-person transmission via mosquitoes in most cases, some can also be spread from animals to people or the reverse, always through the same vector.
According to research published in 2016 in the British medical journal The Lancet, the total annual cost of Dengue amounted to 8 billion Euros.
As well as controlling mosquitoes in residential areas, special attention can be given to controlling mosquitoes near health centres to avoid the spread of transmissible diseases by mosquitoes.
Here are the main diseases studied:

Malaria is a real public health problem in Senegal, as in many other areas of the world.
Numerous efforts have been made by the Senegalese Health Ministry to reduce the impact of the disease on the country’s people and its economy. One of many players involved in this issue, PNLP Sénégal (plan national de lutte contre le paludisme au Sénégal or National Malaria Control Plan in Senegal) seeks to find effective solutions for controlling the proliferation of mosquitoes, while still protecting the environment.
Against this backdrop, Qista set up the ambitious MONIPREV project to combat mosquito bites in areas where malaria spreads in Senegal. The installation of 104 mosquito traps in the Kaolack region sought both to capture as many mosquitoes as possible and to analyse the data collected by the traps to predict the risks of the spread of epidemics.
The presence of mosquitoes on the planet could simply be dismissed as an inconvenience in some more northerly regions were they not also a veritable source of harm to agroeconomic development.
The proliferation of mosquitoes poses 3 major economic challenges:
Identification of infestation zones is facilitated through preliminary research and field research carried out by Qista experts. Mosquito control campaigns can then be prioritised geographically, monitored by Qista.

In his book “La lutte contre les moustiques nuisants et vecteurs de maladies “, Frédéric Darriet, a medical entomologist at the Institut de Recherche pour le Développement, explains that the combination of mosquitoes, disease and people is a real problem for humanity and is detrimental to economic development in affected areas.
“ Diseases always have a negative impact on a region’s economic activities. A sick person cannot tend to their crops or even go to their workplace. It creates human suffering which has repercussions on the family income which itself determines how much food there is to eat, levels of hygiene and everyday comforts.
If such a situation is prolonged, the family unit and even an entire village community becomes weaker. “
In terms of entire countries, it is easy to imagine that the spread of vector-borne diseases by mosquitoes can represent a real reduction in production forces and can considerably hinder the development of urban and agricultural areas.
When it comes to controlling mosquitoes on a large scale, the effective solutions are often rarely environmentally-friendly.

Quita traps only capture female mosquitoes which are looking for prey. Male mosquitoes and females which are not hunting are not captured because they are not targeted and attracted by the olfactory lures.
Qista traps release CO₂ obtained from recovery. Its solution in no way requires the creation of carbon dioxide and the amount of gas emitted is equivalent to that of a human being.
Unlike what can happen with the use of pesticides, no resistance phenomenon is possible with the Qista solution as no insecticides are used. The mosquitoes are captured and simply do not reproduce.
WANT TO KNOW MORE ABOUT QISTA’S TECHNOLOGY?
Our experts can provide a customised presentation and assist you with preparing a large-scale mosquito control project for installation anywhere in the world.
*cost of a local call in France